Linux kernel compilation (for mini6410 board)
Before starting make sure to have installed in your system an ARM GCC toolchain.
Contents
Download Kernel sources
Get from the mini6410 support DVD, the FriendlyARM ftp or the links in this page the source of the linux kernel. These versions are patched and already include a good configured.
| Name | Version | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| FriendlyARM 2.6.38 | 2.6.38 | 2012.09.04 | Original FriendlyARM kernel |
| FriendlyARM 2.6.38 gcc patched | 2.6.38 | 2013.04.22 | Patched to work with GCC 4.7+ versions |
| TuxamitoSoftware 2.6.38 - TS001 | 2.6.38 | 2013.04.24 | Based on the FriendlyARM kernel: - Patched to work with GCC 4.7+ versions - Exposure of sysfs GPIO - Enabled 1-wire protocol - Enabled i2c - Enabled SPI (not exposed automatically) - Enabled NFSv4 network file system - Enabled ext4 file system - Removed many debugging options - Enabled USB Wireless devices - Reduce creation of logs - Removed INITRAMFS |
Uncompress the sources
Uncompress the kernel source file with the command
tar xzvf linux-xxx.tar.gz
or
tar Xzvf linux-xxx.tar.xz
depending on the ending of the file (tar.gz vs tar.xz)
And then cd into de directory:
cd linux-xxx
Configure the kernel
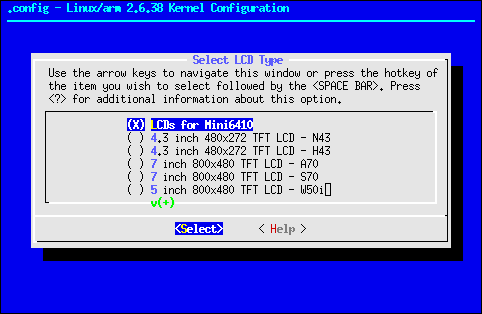
These kernels are patched with drivers to address hardware in the mini6410 board, but we can do some configuration to for example select the LCD (if any) attached to our board:
- Make sure the configuration file is active:
cp config_linux_mini6410 .config - Enter the configuration menul
make menuconfig
(Note that you might need to install ncurses library, libncurses5-dev in Ubuntu / Debian) - Surf the menu to Device Drivers -> Graphics Support -> Support for frame buffer devices -> S3C Framebuffer Support (eXtended) -> Select LCD Type and chose the correct LCD.
- Exit the menu saving the changes.
Compile the kernel
Execute:
make
The compiled kernel is the file zImage in the directory arch/arm/boot/zImage inside the kernel sources directory.